Как я могу переместить окно из невидимого видового экрана в текущий, не переключая видовые окна
Я использую 15.04 с Unity и 4 виртуальными рабочими столами.
Когда я открыл окно на рабочем столе 1 и просматривал рабочий стол 2 (например), есть ли способ легко заставить это окно с рабочего стола 1 отображаться на рабочем столе 2 без переключения просмотра на рабочий стол 1?
Поэтому я хочу получить окно с текущего невидимого рабочего стола на свой активный рабочий стол, не видя невидимый рабочий стол (и, в конечном счете, другие открытые окна на этом).
Есть ли простой способ добиться этого?
1 ответ
Окна списка, выберите одно, чтобы перейти к текущему рабочему пространству
Когда вызывается приведенный ниже скрипт, он перечисляет все окна во всех рабочих пространствах. Выберите один и нажмите OK, чтобы переместить окно в текущее рабочее пространство и поднять его. По умолчанию он перемещает окно в положение 100 (Икс), 100 (У)
Сценарий является относительно простым в результате использования обоих wmctrl а также xdotool, В то время как wmctrl используется для отображения всех окон, xdotool просто перемещает их в предопределенную позицию в текущем рабочем пространстве "не задавая вопросов" по размеру окна (в отличие от wmctrl) и относительные положения обоих рабочих пространств друг к другу.
Более точное позиционирование окна, в соответствии с положением в его исходном рабочем пространстве, вполне возможно, но также умножит необходимый код (как, например, здесь). Я предполагаю, что в большинстве ситуаций это подойдет.
Пример:
Я нахожусь на рабочем месте 8, в то время как у меня есть gedit Окно в рабочей области 1. Вызов скрипта выводит список окон:
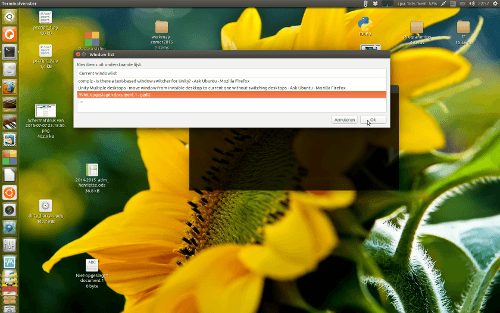
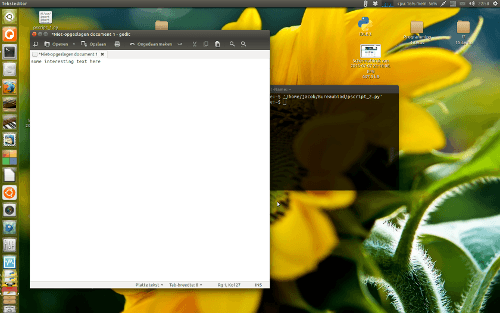
выбор окна Gedit переместит его в текущую рабочую область:
Сценарий
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import subprocess
import socket
import time
def get(command):
return subprocess.check_output(["/bin/bash", "-c", command]).decode("utf-8")
def check_window(w_id):
w_type = get("xprop -id "+w_id)
if " _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_NORMAL" in w_type:
return True
else:
return False
# split wmctrl output by machine name
wlist = [l.split(socket.gethostname()) for l in get("wmctrl -l").splitlines()]
# extract window -id from first section
wlist = [[wlist[i][0].split()[0], wlist[i][-1].strip()] for i, l in enumerate(wlist)]
# filter only "real, normal" windows
wlist = [w for w in wlist if check_window(w[0]) == True]
# create columns for zenity list
cols = (" ").join(['"'+w[1]+'" '+'"'+w[0]+'"' for w in wlist])
# calculate height and width for the zenity window, according to window names and list length
h = str(140+(len(wlist)*23))
w = str((max([len(w[-1]) for w in wlist])*8))
# define the zenity window
cmd = "zenity --list --hide-column=2 --print-column=2 "+\
"--title='Window list' --column='Current windowlist' "+\
"--column='wid' --height="+h+" --width="+w+" "+cols
try:
# call the window
w_id = get(cmd).split("|")[-1].strip()
# move the selected window to the current workspace
subprocess.Popen(["xdotool", "windowmove", "--sync", w_id, "100", "100"])
# raise it (the command below alone should do the job, but sometimes fails
# on firefox windows without first moving the window).
subprocess.Popen(["wmctrl", "-iR", w_id])
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
pass
Как пользоваться
Скрипт нуждается в обоих
wmctrlа такжеxdotoolsudo apt-get install wmctrl xdotoolскопируйте скрипт в пустой файл, сваи как
move_windows.pyПротестируйте его командой:
python3 /path/to/move_windows.pyдолжно появиться окно со списком открытых в данный момент окон:
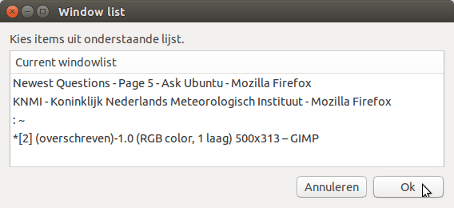
выберите один, чтобы увидеть, перемещается ли он в текущее рабочее пространство и правильно ли поднимается.
Если все работает нормально, добавьте его к сочетанию клавиш: выберите: "Системные настройки" > "Клавиатура" > "Ярлыки" > "Пользовательские ярлыки". Нажмите "+" и добавьте команду:
python3 /path/to/move_windows.py
Заметка
Размер zenity Окно, в котором перечислены текущие окна, устанавливается автоматически. Скрипт ищет самое длинное имя окна и количество строк (окон) и соответственно устанавливает размер.
РЕДАКТИРОВАТЬ
Как и просили в комментарии, ниже версии, в которой zenity Окно списка содержит больше информации: текущее рабочее пространство целевых окон и приложений, которым оно принадлежит.
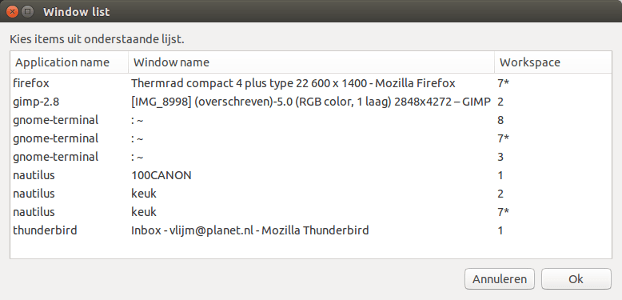
Как упоминалось выше, информация об относительных / абсолютных позициях рабочего пространства приводит к более "существенному" объему кода, но, к счастью, я мог использовать этот более ранний ответ в качестве основы.
Как пользоваться
Использование практически такое же, как в первой версии скрипта (см. Выше), но команда должна включать предпочтительный вариант сортировки. Запустите его одной из команд:
python3 /path/to/move_windows.py -app
отсортировать список по приложению,
python3 /path/to/move_windows.py -ws
отсортировать список по рабочему пространству и
python3 /path/to/move_windows.py -win
отсортировать список по имени окна.
Сценарий:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import subprocess
import socket
import sys
arg = sys.argv[1]
# list (column) header titles and their (data) position in the produced window data list
cols = [["Workspace", -1], ["Application name", -2] , ["Window name", -3]]
# rearrange columns, depending on the chosen option
if arg == "-app":
cols = [cols[1], cols[2], cols[0]]
elif arg == "-ws":
cols = [cols[0], cols[2], cols[1]]
elif arg == "-win":
cols = [cols[2], cols[1], cols[0]]
# extract headers, list positions, to be used in the zenity list
col1 = cols[0][0]; i1 = cols[0][1]
col2 = cols[1][0]; i2 = cols[1][1]
col3 = cols[2][0]; i3 = cols[2][1]
# just a helper function
get = lambda cmd: subprocess.check_output([
"/bin/bash", "-c", cmd
]).decode("utf-8")
# analyse viewport data, to be able to calculate relative/absolute position of windows
# and current viewport
def get_spandata():
xr = get("xrandr").split(); pos = xr.index("current")
res = [int(xr[pos+1]), int(xr[pos+3].replace(",", "") )]
spandata = get("wmctrl -d").split()
span = [int(n) for n in spandata[3].split("x")]
cols = int(span[0]/res[0]); rows = int(span[1]/res[1])
curr_vector = [int(n) for n in spandata[5].split(",")]
curr_viewport = int((curr_vector[1]/res[1])*cols + (curr_vector[0]/res[0])+1)
return {"resolution": res, "n_columns": cols, "vector": curr_vector, "current_viewport": curr_viewport}
posdata = get_spandata()
vector = posdata["vector"]; cols = posdata["n_columns"]
res = posdata["resolution"]; currvp = posdata["current_viewport"]
# function to distinguish "normal" windows from other types (like the desktop etc)
def check_window(w_id):
w_type = get("xprop -id "+w_id)
if " _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_NORMAL" in w_type:
return True
else:
return False
# split windowdata by machine name
mach_name = socket.gethostname()
wlist = [[l.strip() for l in w.split(mach_name)] for w in get("wmctrl -lpG").splitlines()]
# split first section of window data
for i, w in enumerate(wlist):
wlist[i][0] = wlist[i][0].split()
# filter only "real" windows
real_wlist = [w for w in wlist if check_window(w[0][0]) == True]
# adding the viewport to the window's data
for w in real_wlist:
w.append(get("ps -p "+w[0][2]+" -o comm=").strip())
loc_rel = [int(n) for n in w[0][3:5]]
loc_abs = [loc_rel[0]+vector[0], loc_rel[1]+vector[1]]
abs_viewport = int((loc_abs[1]/res[1])*cols + (loc_abs[0]/res[0])+1)
abs_viewport = str(abs_viewport)+"*" if abs_viewport == currvp else str(abs_viewport)
w.append(abs_viewport)
# set sorting rules
if arg == "-app":
real_wlist.sort(key=lambda x: x[-2])
elif arg == "-ws":
real_wlist.sort(key=lambda x: x[-1])
elif arg == "-win":
real_wlist.sort(key=lambda x: x[-3])
# calculate width and height of the zenity window:
# height = 140px + 23px per line
h = str(140+(len(real_wlist)*23))
# width = 250px + 8px per character (of the longest window title)
w = str(250+(max([len(w[-3]) for w in real_wlist])*8))
# define the zenity window's content
cmd = "zenity --list --hide-column=4 --print-column=4 --title='Window list' "\
"--width="+w+" --height="+h+" --column='"+col1+"' --column='"+col2+"' --column='"+col3+\
"' --column='w_id' "+(" ").join([(" ").join([
'"'+w[i1]+'"','"'+w[i2]+'"','"'+w[i3]+'"','"'+w[0][0]+'"'
]) for w in real_wlist])
# finally, call the window list
try:
w_id = subprocess.check_output(["/bin/bash", "-c", cmd]).decode("utf-8").split("|")[0]
subprocess.Popen(["xdotool", "windowmove", "--sync", w_id, "100", "100"])
subprocess.Popen(["wmctrl", "-iR", w_id])
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
pass
РЕДАКТИРОВАТЬ 2: 15.04 конкретных
Выход использованных ps команда, кажется, изменилась для gnome-terminal в 15.04. Поэтому в 15.04 название приложения gnome-terminal не был правильно отображен в сценарии выше. Версия ниже выводит имя приложения из WM_CLASS, как на выходе xprop команда:
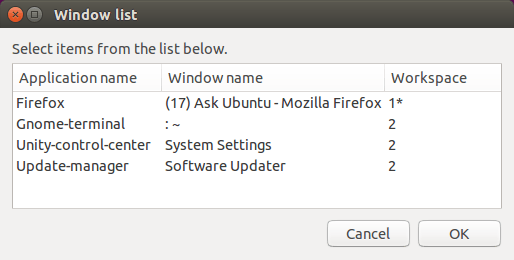
Использование точно такое же, как в (втором) скрипте выше:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import subprocess
import socket
import sys
arg = sys.argv[1]
# list (column) header titles and their (data) position in the produced window data list
cols = [["Workspace", -1], ["Application name", -2] , ["Window name", -3]]
# rearrange columns, depending on the chosen option
if arg == "-app":
cols = [cols[1], cols[2], cols[0]]
elif arg == "-ws":
cols = [cols[0], cols[2], cols[1]]
elif arg == "-win":
cols = [cols[2], cols[1], cols[0]]
# extract headers, list positions, to be used in the zenity list
col1 = cols[0][0]; i1 = cols[0][1]
col2 = cols[1][0]; i2 = cols[1][1]
col3 = cols[2][0]; i3 = cols[2][1]
# just a helper function
get = lambda cmd: subprocess.check_output([
"/bin/bash", "-c", cmd
]).decode("utf-8")
# analyse viewport data, to be able to calculate relative/absolute position of windows
# and current viewport
def get_spandata():
xr = get("xrandr").split(); pos = xr.index("current")
res = [int(xr[pos+1]), int(xr[pos+3].replace(",", "") )]
spandata = get("wmctrl -d").split()
span = [int(n) for n in spandata[3].split("x")]
cols = int(span[0]/res[0]); rows = int(span[1]/res[1])
curr_vector = [int(n) for n in spandata[5].split(",")]
curr_viewport = int((curr_vector[1]/res[1])*cols + (curr_vector[0]/res[0])+1)
return {"resolution": res, "n_columns": cols, "vector": curr_vector, "current_viewport": curr_viewport}
posdata = get_spandata()
vector = posdata["vector"]; cols = posdata["n_columns"]
res = posdata["resolution"]; currvp = posdata["current_viewport"]
# function to distinguish "normal" windows from other types (like the desktop etc)
def check_window(w_id):
w_type = get("xprop -id "+w_id)
if " _NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_NORMAL" in w_type:
cl = [l.replace('"', '').split(",")[-1].strip()\
for l in w_type.splitlines() if "WM_CLASS(STRING)" in l][0]
return (True, cl)
else:
return (False, "")
# split windowdata by machine name
mach_name = socket.gethostname()
wlist = [[l.strip() for l in w.split(mach_name)] for w in get("wmctrl -lpG").splitlines()]
# split first section of window data
for i, w in enumerate(wlist):
wlist[i][0] = wlist[i][0].split()
# filter only "real" windows
real_wlist = [w+[check_window(w[0][0])[1]] for w in wlist if check_window(w[0][0])[0] == True]
# adding the viewport to the window's data
for w in real_wlist:
loc_rel = [int(n) for n in w[0][3:5]]
loc_abs = [loc_rel[0]+vector[0], loc_rel[1]+vector[1]]
abs_viewport = int((loc_abs[1]/res[1])*cols + (loc_abs[0]/res[0])+1)
abs_viewport = str(abs_viewport)+"*" if abs_viewport == currvp else str(abs_viewport)
w.append(abs_viewport)
# set sorting rules
if arg == "-app":
real_wlist.sort(key=lambda x: x[-2])
elif arg == "-ws":
real_wlist.sort(key=lambda x: x[-1])
elif arg == "-win":
real_wlist.sort(key=lambda x: x[-3])
# calculate width and height of the zenity window:
# height = 140px + 23px per line
h = str(140+(len(real_wlist)*23))
# width = 250px + 8px per character (of the longest window title)
w = str(250+(max([len(w[-3]) for w in real_wlist])*8))
# define the zenity window's content
cmd = "zenity --list --hide-column=4 --print-column=4 --title='Window list' "\
"--width="+w+" --height="+h+" --column='"+col1+"' --column='"+col2+"' --column='"+col3+\
"' --column='w_id' "+(" ").join([(" ").join([
'"'+w[i1]+'"','"'+w[i2]+'"','"'+w[i3]+'"','"'+w[0][0]+'"'
]) for w in real_wlist])
# finally, call the window list
try:
w_id = subprocess.check_output(["/bin/bash", "-c", cmd]).decode("utf-8").split("|")[0]
subprocess.Popen(["xdotool", "windowmove", "--sync", w_id, "100", "100"])
subprocess.Popen(["wmctrl", "-iR", w_id])
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
pass